International Space Station (ISS)
About the International Space Station (ISS)
- The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest single structure humans ever put into space.
- Its main construction was completed between 1998 and 2011, although the station continually evolves to include new missions and experiments.
- It has been continuously occupied since Nov. 2, 2000.
- The space station is parked at Low Earth Orbit (LEO) at approximately 350 km above the Earth.
- The ISS makes multiple orbits around the Earth every day.
- The ISS includes contributions from 15 nations. NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia) and the European Space Agency are the major partners of the space station who contribute most of the funding; the other partners are the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency and the Canadian Space Agency.
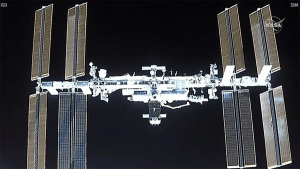
- The ISS serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which crew members conduct experiments in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and other fields.
- Astronauts spend most of their time on the ISS performing experiments and maintenance. Sometimes, this requires that they venture on spacewalks to perform repairs.
- The station is divided into two sections, the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), which is operated by Russia, and the United States Orbital Segment (USOS), which is shared by many nations.
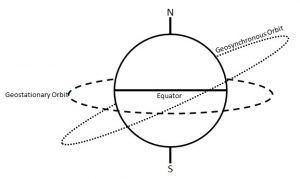
Types of Orbits around the earthGeostationary Orbit (GEO)
Geosynchronous Orbit
Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
Polar Orbits
|
Why in News?
- SpaceX in association with NASA launched its Crew Dragon capsule on top of its Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station (ISS).
News in detail
- The mission is ‘historic’ because this is the first-ever time that a private spacecraft company — Space X — used its own rocket to put humans into space.
- The mission is expected to last 30-90 days, following which the two astronauts will depart from the International Space Station by boarding the Crew Dragon.
- This is the first time that astronauts have been launched from US soil since the STS-135 mission on July 8, 2011, following which all astronauts were flown to the International Space Station in Russia’s Soyuz Capsule.
What is Falcon 9?
- Falcon 9 is a reusable, two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX for the reliable and safe transport of people and payloads into Earth orbit and beyond.
- Falcon 9 is the world’s first orbital class reusable rocket. Orbital class rockets are those that put a spacecraft/satellite in an orbit around the Earth.
- Reusability allows SpaceX to refly the most expensive parts of the rocket, which in turn drives down the cost of space access.


[…] To know more about International Space Station and different orbits of Earth- https://officerspulse.com/international-space-station-iss/ […]