Auroras
What is an Aurora?
- An aurora is a natural phenomenon which is characterized by a display of a natural-coloured (green, red, yellow or white) light in the sky.
- It is a light show which is caused when electrically-charged particles from the sun collide with particles from gasses such as oxygen and nitrogen present in the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Aurora is sometimes referred to as ‘polar light’.
- It is predominantly seen in the regions of high altitudes like the Arctic and Antarctic.
What causes an Aurora?
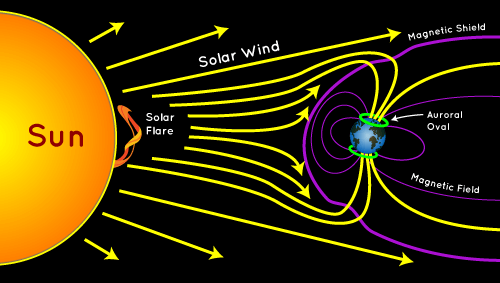
- An aurora is caused by the streams of electrified particles (which are emitted by the sun) trapped in the magnetic field of the earth.
- It is produced when this magnetosphere is disturbed by the solar wind carrying the charged particles.
- Auroras are seen in latitudes of around 70 degrees. They generally occur in a band known as ‘auroral zone’.
- The auroral zone is 3 to 6 degrees wide in latitude. It lies between 10 and 20 degrees from the geomagnetic poles.
- This is visible quite clearly during the night. Auroras can sometimes be seen at latitudes below the actual auroral zone.
- Auroras can appear in various forms like streamers, patches, arcs, scattered light, diffused light etc.
- The brightest and the most distinctive of all forms of auroras are the ones which are curtain-like in the shape of an arc, extending in the east-west direction.
- This natural light effect is known as ‘aurora borealis’ in northern altitudes, while the effect in the southern latitudes is known as ‘aurora australis’.
- Aurora borealis is also known as ‘Northern lights’. Similarly, aurora australis is also known as ‘Southern lights’.
Tag:space
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
