OPEC
About OPEC arrangement
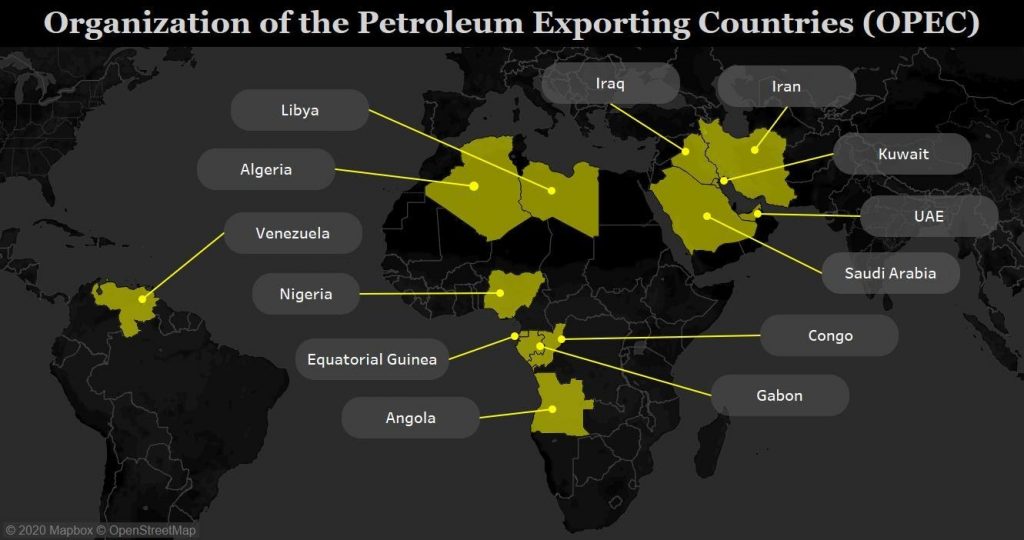
- The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is a group consisting of 13 of the world’s major oil-exporting nations.
- Countries that belong to OPEC include Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela (the five founders), plus the United Arab Emirates, Libya, Algeria, Nigeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea and Gabon.
- Note: Ecuador and Qatar terminated their membership of OPEC recently.
- OPEC was founded in 1960 to coordinate the petroleum policies of its members and to provide member states with technical and economic aid.
- OPEC is used to work as a cartel and fix prices in a favourable band. It could bring down prices by increasing oil production and raise prices by cutting production.
OPEC Plus
The 2014 oil crisis, which was accentuated by oversupply of crude, brought down prices below $30 a barrel. Since then, OPEC has been working with non-OPEC countries like Russia, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Sudan and South Sudan to fix the global prices and supply.
Known as the “OPEC Plus” arrangement, this alliance kept production lower and pumped up the prices.
Why in News?
- Oil prices surged to multi-year highs, after OPEC+ producers cancelled a meeting due to clashes over plans to increase supply to meet rising global demand.
- Discussions dissolved after Saudi Arabia, the largest OPEC producer, and the United Arab Emirates were unable to agree over the terms for increasing supply.
Reference:
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
