DNA Profiling
About
- DNA Profiling (also known as DNA fingerprinting or genetic fingerprinting) is a forensic technique used to identify individuals by analyzing unique characteristics of their DNA.
- While human DNA is 99.9% identical, the remaining 0.1% includes unique sequences called Short Tandem Repeats (STRs) or Microsatellites, which are crucial for DNA Profiling.
- DNA can be obtained from any biological material since the same DNA sequence is present in every cell of the body.
- Common sources include saliva, semen, vaginal fluids, blood, body tissues, teeth, hair, and bones. However, the amount of DNA varies across these materials.
- Blood and saliva are rich in DNA, while teeth and hair roots contain less DNA, making them less ideal for extraction.
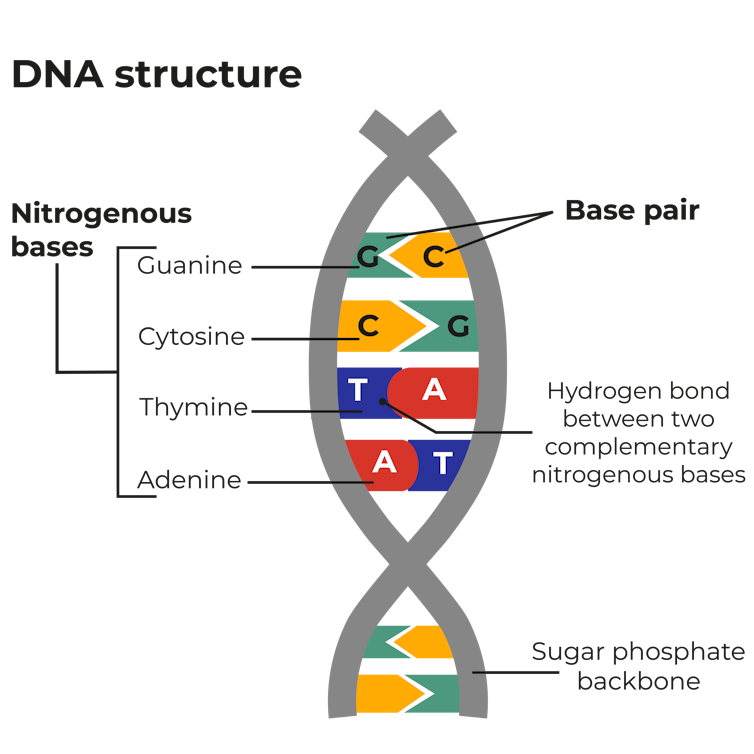
DNA:
|
Applications of DNA Profiling
- Criminal Investigations: Used to match DNA from crime scenes (e.g., blood, hair) with suspects, helping to identify or exclude individuals involved in a crime.
- Paternity and Maternity Testing: Confirms biological relationships, establishing parentage for legal, medical, or personal reasons.
- Identification of Missing Persons: Helps in identifying unknown or missing individuals, especially in cases of natural disasters, accidents, or war.
- Identification of racial groups: DNA fingerprinting helps identify genetic differences among racial groups, which can provide insights into human evolution and migration patterns.
- Diagnosis of inherited disorders: DNA fingerprinting is useful in diagnosis of inherited disorders which include Hungtington’s diseases, sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, cystic fibrosis, hemophilia etc.,
Did you know?
|
DNA Barcoding vs DNA Fingerprinting:
Applications of DNA Barcoding:
|
Did you know?
|
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments