Nipah
About Nipah infection
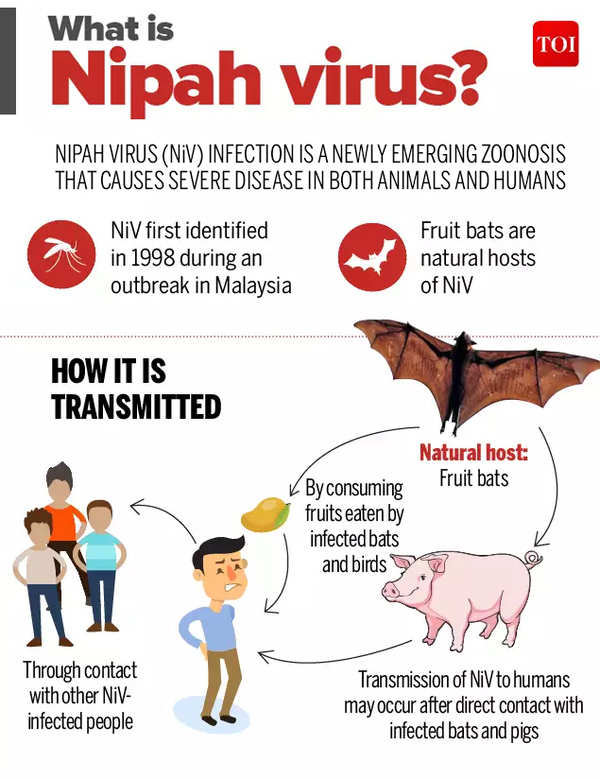
- It is a viral infection caused by the Nipah virus (NiV).
- Fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family are the natural host of Nipah virus.
- The disease was first identified in 1998 during an outbreak in Malaysia. Later, Nipah outbreaks have been reported in Singapore, Bangladesh and India.
Transmission
- It is a zoonotic virus (transmitted from animals to humans) which can also be transmitted through contaminated food or directly between people.
- Consumption of fruits or fruit products (such as raw date palm juice) contaminated with urine or saliva from infected fruit bats is the most likely source of infection.
- In infected people, it causes a range of illnesses from asymptomatic infection to acute respiratory infection (mild, severe), and fatal encephalitis (inflammation in the brain).
- The virus can also cause severe disease in animals such as pigs, resulting in significant economic losses for farmers.
Treatment
- There are currently no drugs or vaccines specific for Nipah virus infection.
- The primary treatment for humans is supportive care.
Preventing the Nipah virus involves infection control measures like using protective equipment, disinfecting surfaces, and avoiding sick animals or areas with known Nipah virus outbreaks
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
