Ground water extraction
Context
- Excessive groundwater extraction is triggering land subsidence in the Indo – Gangetic plain.
Land subsidence
- Land subsidence refers to the gradual sinking or settling of the Earth’s surface, often caused by the removal of groundwater, the extraction of minerals, oil and gas, or natural geological processes.
- It can also occur as a result of human activities, such as construction, mining, and the drainage of wetlands.
- Land subsidence can have various negative impacts on infrastructure, ecosystems, and communities.
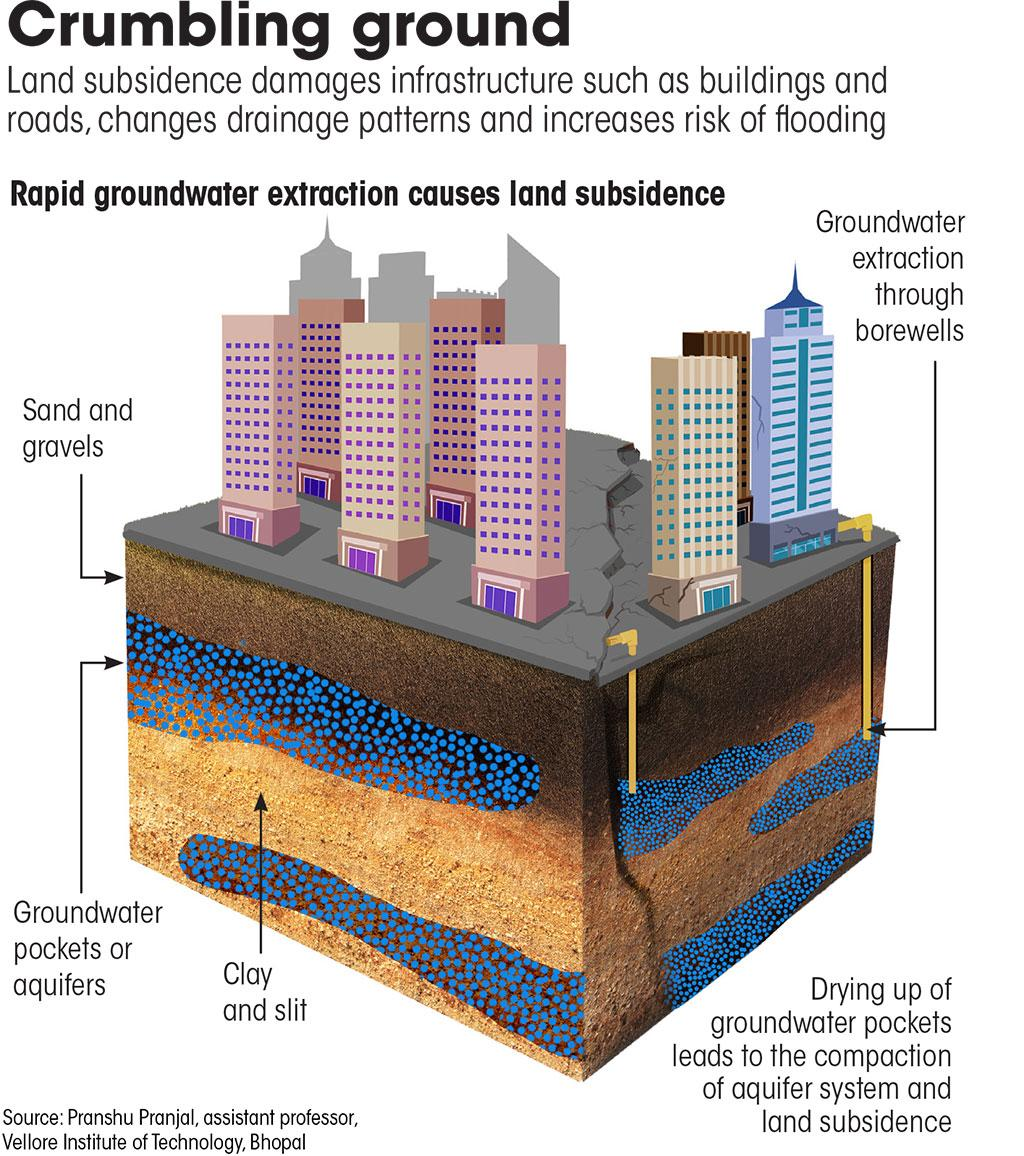
Ground water extraction and Land subsidence
- Groundwater generally resides in pores or aquifers within the soil.
- When large amounts of groundwater are extracted year after year, a void is created in the pores.
- This causes collapse or compaction of the soil, leading to land subsidence.
- The Indo – Gangetic plain, which has stratified layers of sand and clay, is highly prone to subsidence.
Global crisis
- The San Joaquin Valley of California, land continues to sink by 0.3 m per year due to excessive pumping of groundwater for a commercial orchard, which has caused permanent subsidence and landslides in the area.
- Jakarta is considered the world’s fastest sinking city. With 40 percent of the city already below sea level, it is predicted that by 2050, some 95 per cent of North Jakarta will be underwater.
- Bangkok in Thailand and Ho Chi Minh City in Vietnam are also sinking, with subsidence rates of up to 2 cm and 5 cm per year, respectively.
Threats posed by land subsidence
- As per the report, ‘Sinking cities: Two ways to fight land subsidence“, 77 per cent of land subsidence cases are caused by human activities, with groundwater extraction accounting for 60 per cent.
- Land subsidence can damage buildings, roads, bridges, pipelines, and other infrastructure.
- In coastal areas, land subsidence can lower the elevation of land, increasing the vulnerability to flooding
- Subsidence can alter drainage patterns, impacting wetlands, rivers, and aquatic ecosystems.
- The impacts of land subsidence can lead to displacement of communities, economic losses due to infrastructure damage, and reduced livelihood opportunities.
Way Forward
- Land subsidence cannot be reversed by groundwater recharge, so, the solution is to arrest the over extraction of groundwater.
- Water budgeting (availability and usage of water is computed) is important for high-risk regions
- It is important to revive water bodies that can aid groundwater recharge
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
