Zoonoses Crucibles
Context
- Livestock diseases have an enormous impact not only on animal health and economy, but also on human health. Further, Livestock house pathogens that can become zoonoses and hence timely detection is necessary to curb outbreaks.
Zoonoses
- According to WHO, Zoonoses are diseases and infections which are naturally transmitted between vertebrate animals and man.
- They may be bacterial, viral, or parasitic, or may involve unconventional agents for the transmission of diseases.
Causes of Zoonotic Diseases
- Deforestation, Habitat loss and Fragmentation has increased the contact between humans and wild animals.
- Zoonoses can occur due to direct contact with body fluids such as blood, saliva, of an infected animal.
- It can also spread due to consumption of contaminated food.
- Overuse of anti-microbials and climate change are other causative factors
Recent findings
- A UN report revealed that in the last 170 years, nine epidemics among livestock have spilled over to people. Frequent outbreaks in recent decades are due to intensification of agriculture.
- Nearly 77 per cent of livestock pathogens are capable of infecting multiple host species, including wildlife and humans.
- Most of the increase in human and livestock densities are expected to occur in developing countries where disease surveillance, pest control, sanitation, and medical and veterinary care are limited.
Emergence of various Zoonotic diseases at Animal Human Interface
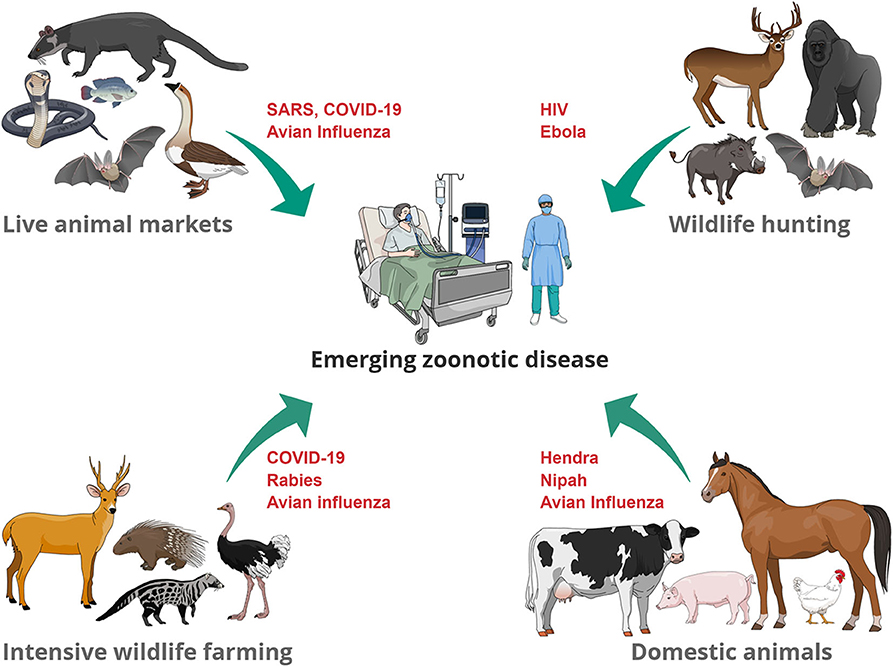
Indian Scenario
- India suffers from the highest zoonotic disease burden along with Ethiopia, Nigeria and Tanzania.
- In India out of the 13 livestock diseases monitored by the National Institute of Veterinary Epidemiology and Disease Informatics (NIVEDI), four are zoonotic, namely, anthrax, babesiosis, fasciolosis and trypanosomiasis.
- To prevent potential disease outbreaks, NIVEDI issues forewarning every month which has above 90 per cent accuracy and has helped stakeholders take preventive measures in time.
National Digital Livestock Mission
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, with the objective of ensuring sustainable development of the livestock sector.
- It aims to tag all major livestock in the country with a unique 12-digit identification (ID) number.
- Details like age, breed, milk yield, vaccinations and dates of artificial insemination and delivery of calf, recorded in a central database.
- Disease modelling and surveillance for prevention and control of livestock diseases will be done through mobile veterinary units, connected with toll free helpline number, 1962.
Other Initiatives
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission was launched for the development and conservation of indigenous breeds through selective breeding in bovine population.
- The National Animal Disease Control Programme was launched to control Foot & Mouth Disease and Brucellosis.
- Livestock Health & Disease Control (LH&DC) Scheme aims to reduce risk to animal health by vaccination against diseases of animals, capacity building of Veterinary services, disease surveillance and strengthening veterinary infrastructure.
Way Forward
- An effective response to emerging zoonotic diseases relies heavily on efficient surveillance and reporting systems.
- Cross-sectoral collaboration is key to understanding and managing public health risks at the human-animal-environment interface and to improve national health security.
- The establishment of effective laboratory systems is critical for surveillance of zoonotic diseases.
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
