Climate change threatens Food but Microscopic Algae offer answers
What is Micro Algae?
- Microalgae are microscopic organisms found in both seawater and freshwater. They are unicellular species which exist individually, or in chains or groups.
- They can be classified as eukaryotic microorganisms or prokaryotic cyanobacteria (blue-green algae)
- These microorganisms perform photosynthesis, which is an important natural mechanism to reduce the atmospheric CO2 concentration.
- Microalgae, together with bacteria, form the base of the food web and provide energy for all the trophic levels above them.
Why in news?
- As per study published by IPCC, the emerging and predicted impacts on agriculture and food supplies are stark. Eg: The heat waves, drought and increasing rainfall variability could adversely affect crop yields and livestock productivity which in turn could cause problems with food availability and nutritional quality, as well as risks of malnutrition and hunger. Thus Consumers, businesses and researchers have shown growing interest in microalgae in recent years.
- A new academic paper is set out to provide provisional answers. It reviewed the available evidence on microalgae as food supplements, livestock feeds, biofertilizers, biostimulants and biochar feedstocks. It then assessed the potential of these five microalgae applications to serve as the basis for climate actions.
What is the potential of Agri-food Microalgae applications?
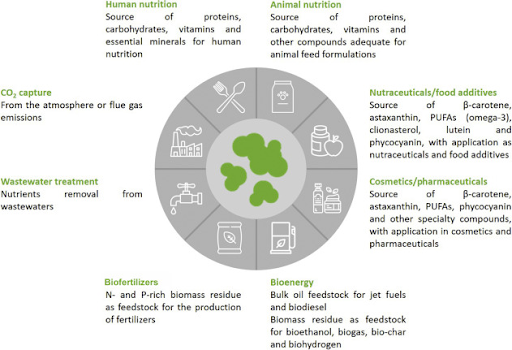
- Using Microalgae as Food Supplement
- Microalgae have been used as traditional foods in various countries where suitable species occur naturally, such as Mexico and Chad.
- As foods, microalgae can be potent sources of nutrients, including high-quality proteins, lipids and vitamins.
- Nowadays microalgae food supplements are principally eaten by health-conscious consumers as they can also be used to address malnutrition and to improve health in places where diet is poor.
- Using Microalgae as Livestock feeds
- Novel feeds like microalgae, seaweed and insects offer options to improve the sustainability of livestock production by providing protein-rich complements to staple feeds like grasses and feed crops.
- Eg: Microalgae feeds have been tested on cattle, goats, sheep, pigs, poultry and fish. The results have typically included improved productivity, better nutritional quality of products, or both.
- Microalgae could also provide a secure source of feed in places where livestock deaths linked to climate change are a growing concern.
- Using Microalgae as Biofertilizer or Biostimulants
- Global crop production continues to rely heavily on chemical fertilizers to boost crop productivity but such products can sometimes undermine agricultural sustainability.
- Biofertilisers and biostimulants are natural alternative options for boosting crop production as Biofertilisers provide nutrients to plants and Biostimulants promote plant growth by stimulating biological or chemical processes in plants or microbes associated with roots.
- Early studies of microalgae-based biofertilizers and biostimulants suggest they can boost productivity while also building the resilience of crops to climate-related stresses like elevated temperatures, water scarcity and soil salinity.
- Using Microalgae as Biochar Feedstocks
- Biochar was a traditional soil management tool in some cultures. Microalgae could support crop production by using algal biomass to make biochar, or charred biomass.
- Applying biochar to fields can improve soil fertility and enhance soil’s capacity to hold water. Such effects could help crops cope with climate change impacts like erratic rainfall and extreme weather events.
- Other applications
- Microalgae also has a wide application in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, being used as a source of essential amino acids, antioxidants, pigments, and vitamins.
- Microalgae can accumulate high amounts of lipids that can be used for biodiesel production and after fatty acids extraction, biomass residue can be used for the production of bio-oil, bio-crude, ethanol, and methane.
Conclusion
- These five agri-food applications of microalgae could be seen as possible ways to enhance the climate resilience of food production, and hence as climate change adaptation measures as they offer options to help secure both food supplies and agricultural livelihoods despite climate change.
- These applications could be framed as climate actions but more research is needed to explore and verify this potential, and to examine issues like consumer acceptance and managing possible contamination risks.
- References:
- https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/energy-and-environment/climate-change-threatens-food-but-microscopic-algae-offer-answers/article65909004.ece
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/microalgae
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microalgae
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
