Fortification of Rice
What is Fortification of Food?
- Fortification is the addition of key vitamins and minerals such as iron, iodine, zinc, Vitamin A & D to staple foods such as rice, milk and salt to improve their nutritional content. These nutrients may or may not have been originally present in the food before processing.
- It is a cost-effective strategy for improving diets and for the prevention and control of micronutrient deficiencies.
- It can be carried out by food manufacturers, or by governments as a public health policy which aims to reduce the number of people with dietary deficiencies within a population.
Need for Food Fortification
- 70% of people in India do not consume enough micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals.
- According to the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5):
- 67 percent of children (6-59 months) are anaemic
- 57 percent women in the reproductive age group are anaemic
- every third child still suffers from chronic undernourishment, and every fifth child is acutely malnourished.
- Deficiency of micronutrients or micronutrient malnutrition, also known as “hidden hunger”, is a serious health risk.
- Those who are economically disadvantaged do not have access to safe and nutritious food. Others either do not consume a balanced diet or lack variety in the diet because of which they do not get adequate micronutrients.
- Often, there is considerable loss of nutrients during the processing of food. One of the strategies to address these problems is fortification of food.
Benefits of Food Fortification
- Since the nutrients are added to staple foods that are widely consumed, this is an excellent method to improve the health of a large section of the population, all at once.
- It does not require any changes in food habits and patterns of people. It is a socio-culturally acceptable way to deliver nutrients to people.
- It does not alter the characteristics of the food—the taste, the feel, the look.
- It can be implemented quickly as well as show results in improvement of health in a relatively short period of time.
- The Copenhagen Consensus (a conference of prominent economists) estimates that every 1 Rupee spent on fortification results in 9 Rupees in benefits to the economy. Thus it has a high benefit-to-cost ratio.
How does the government use food fortification in various schemes?
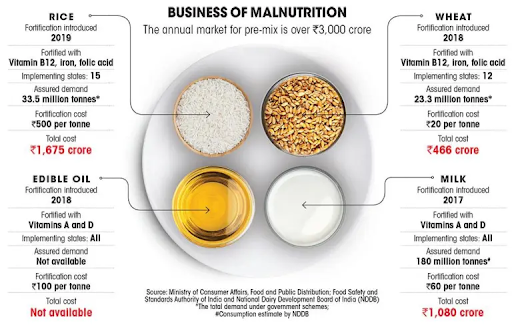
- In 2016, FSSAI operationalized the Food Safety and Standards (Fortification of Foods) Regulations, 2016 for fortifying staples namely
- Wheat Flour and Rice with Iron, Vitamin B12 and Folic Acid,
- Milk and Edible Oil with Vitamins A and D and
- Double Fortified Salt with Iodine and Iron
- The ‘+F’ logo has been notified to identify fortified foods.
- The National Nutritional Strategy of 2017 included food fortification as one of the measures to address anaemia, vitamin A, and iodine deficits.
- The Government is distributing fortified rice through the Integrated Child Development Services and Mid Day Meal Scheme.
Why in News?
- In order to promote the benefits of Fortified Rice while elucidating the concerns about the impact of its consumption among some sections of the population those are vulnerable to Thalassemia and Sickle Cell Anaemia, the Department of Food and Public Distribution (DFPD) has requested various States like Gujarat, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Telangana Rajasthan, Kerala to organize workshop/seminar by the respective State Governments in the sensitive areas of tribal belts and districts that have populations that are vulnerable to Thalassemia and Sickle Cell Anaemia.
- Prime Minister in his address on the 75th Independence Day (15th August, 2021), announced the supply of Fortified Rice in every scheme of Government of India throughout the country by 2024 in a phased manner. Since then, the initiative has made good progress during the last one year.
- Rice Fortification is the process of adding Fortified Rice Kernels (FRK), containing FSSAI prescribed micronutrients (Iron, Folic Acid, Vitamin B12) to normal Rice (Custom Milled Rice) in the ratio of 1:100 (Mixing 1 Kg of FRK with 100 Kg custom milled rice).
- Fortified rice is nearly identical to traditional rice in aroma, taste, and texture. This process is done in the rice mills at the time of milling of rice.
- Fortification of rice is found to be a cost-effective and complementary strategy to increase vitamin and mineral content in diets with low turnaround time (TAT) and a step towards nutritional security and helps in fighting anaemia and malnutrition in the country.
Reference:
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
