Swami Swaroopanand Saraswati
Why in News
- Dwarka peeth Shankaracharya Swami Swaroopanand Saraswati passed away.
About Adi Shankaracharya
- Adi Shankara is said to have been born in Kaladi, Kerala in 788 CE on the bank of the Periyar, the largest river in Kerala.
- He opposed the practice of ritual worship.
- He also felt that when a person’s intellect is cleansed by living an ethical life, self-knowledge is reached.
- He also emphasized on Yamas. Within the Yoga philosophy, the Yamas are the ethical guidelines of right life.
Associated Philosophies
- Maya Theory, Advaita Sidhanta (Non-Dualism), Tarak Brahma.
Advaita Sidhanta
- The theory of Advaita says that the Upanishad actually teaches that the individual soul (called Atman) is not different from Ultimate Reality (called Brahman).
- Adi Shankara also taught that there is only one essential principle called Brahman and everything else is a kind of expression of that one Brahman.
- Because of this theory of one being, his teachings became popular as the “Advaita” (a = not, dvaita = two, means no-two or non-dual).
- In simple words, People who believe in Advaita believe that their soul is not different from Brahman. Here Brahman means reality (consciousness) and not the caste.
- The Advaita Vedanta schools use concepts such as Maya, Brahman, Atman, Avidya and meditation.
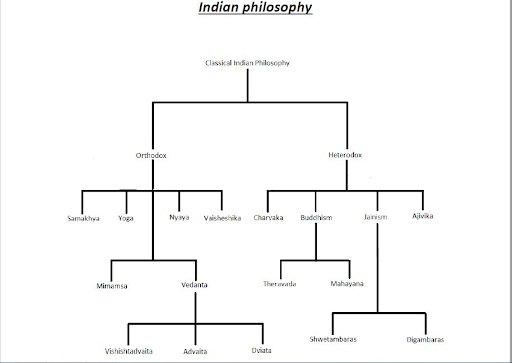
Where Advaita Sidhanta shares similarities with other philosophies
- Mahayana Buddhism says that anyone (including the person in the cycle of samsara) can achieve enlightenment. (In Hinduism, all life goes through birth, life, death, and rebirth and this is known as the cycle of samsara)
- Within Islam there is an idea of annihilation within the divine, Fana and Waḥdat al-Wujūd (Unity of Existence).
Major Works of Shankaracharya
- Commentaries (bhashyas) on 10 Upanishads, the Brahmasutra and the Gita
- Bhajagovinda Stotram
- Nirvana Shatakam
- Poetic works include Vivekachudamani, Maneesha Panchakam, and Saundaryalahiri. Some scholars propose that they are not his works but are his attributions
Contributions of Shankaracharya:
- Shankara is believed to have established Mathas in Sringeri, Dwaraka, Puri, and Badrinath for the spread of Advaita Vedanta.
- Sri Hastamalakacharya as the Acharya of the Govardhana Math in the East.
- Sri Sureshwaracharya as the Acharya of Sringeri Sharada Peetham in the South.
- Sri Padmapadacharya as the Acharya of the Dwaraka Math in the West.
- Sri Totakacharya as the Acharya of Jyotir Math(Joshi Math) in the North.
- Tried to revive Hinduism in India while Buddhism was gaining popularity.
- Shankaracharya emulated both the approach of Jnana and Bhakti at the same time. He revitalized the entire Sanatana Dharma with His siddhanta (approach) called Advaita.
- Thought not a Bhakti saint, he made a foundation for Bhakti movement
Mains Question: Discuss about role and contribution of Adi Sankaracharya in growth of Bhakti movement in India- https://bit.ly/3B6UqTZ
Reference:
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
