Kasturirangan Committee Report on Western Ghats
Major Recommendations
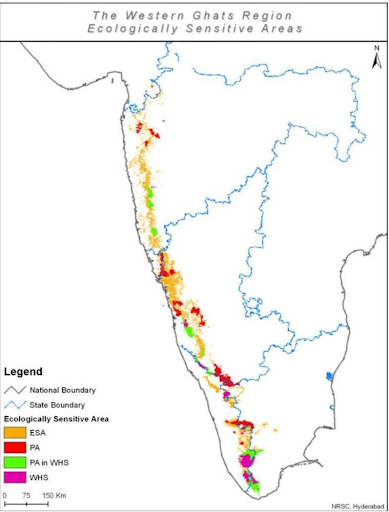
- The Kasturirangan committee report proposes 37 per cent of the total area of Western Ghats, which is roughly 60,000 square kilometres, to be declared as eco-sensitive area (ESA).Out of this, 20,668 sq km of the area falls in Karnataka covering 1,576 villages.
- The report recommended a blanket ban on mining, quarrying, setting up of red category industries and thermal power projects.
- It also stated that the impact of infrastructural projects on the forest and wildlife should be studied before permission is given for these activities.
- It also stated that the UNESCO Heritage tag is an opportunity to build global and domestic recognition of the enormous natural wealth that exists in the Western Ghats.
- The 39 sites are located across the Western Ghats and distributed across the states Kerala (19), Karnataka (10), Tamil Nadu (6) and Maharashtra (4).
- The state of Karnataka has the highest percentage of the ESA- 46.50 per cent.
- The boundary of the sites, are in most cases, boundaries of the legally demarcated national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, tiger reserves and forest divisions and therefore, already accorded with high level of protection. Hence, the state governments should view this development and build a plan to protect, conserve and value the resources and opportunities of the region.
Why have the successive governments in Karnataka rejected the report?
- The state government believes that implementation of the report will halt the developmental activities in the region.
- People of the region have adopted agriculture and horticultural activities in an eco-friendly manner and Priority has been accorded for environment protection under the Forest Protection Act. In this background bringing one more law that would affect the livelihood of the local people.
- The political representatives from Uttara Kannada district have always opposed the Kasturirangan report since 600-plus villages will fall under the eco-sensitive area if the report is implemented.
Why in News?
- Recently, the Karnataka Chief Minister informed the Centre that the state is opposed to the Kasturirangan Committee report on Western Ghats.
Additional Details
About Eco-sensitive Areas(ESAs)
- ESAs are defined as those areas that are ecologically and economically important, but vulnerable even to mild disturbances, and hence demand careful management.
- As a general principle, land falling within 10 kms of the boundaries of the National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries are categorised as Eco-Fragile Zones or Eco-sensitive Zones.
- They are declared under the Environment Protection Act, 1986.
- The purpose of declaring Eco-sensitive Zones around National parks and Sanctuaries is to create some kind of ”Shock Absorber” for the Protected Areas. They would also act as a transition zone from areas of high protection to areas involving lesser protection.
- The activities in the eco-sensitive zones would be of a regulatory nature rather than prohibitive nature, unless and otherwise so required.
Reference:
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
