IRNSS
Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) – NavIC
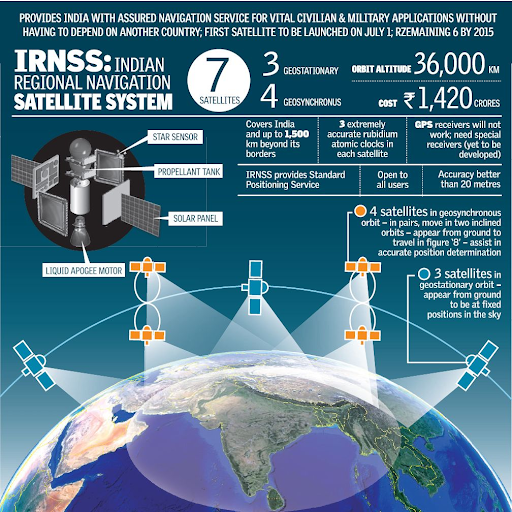
- IRNSS is an independent regional navigation satellite system developed by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO).
- In April 2016, with the last launch of the constellation’s satellite, IRNSS was renamed Navigation Indian Constellation (NAVIC).
Range of NavIC
- It is designed to provide accurate position information service to users in India as well as the region extending up to 1500 km from its boundary, which is its primary service area.
- Beyond that lies an Extended Service Area, that can extend up to the edges of the area enclosed by the rectangle imagined by latitudes 30 degrees South and 50 degrees North, and longitudes 30 degrees East and 130 degrees East.
- IRNSS will provide two types of services, namely, Standard Positioning Service (SPS) which is provided to all the users and Restricted Service (RS), which is an encrypted service provided only to the authorised users.
- The IRNSS System is expected to provide a position accuracy of better than 20 m in the primary service area.
- The space segment consists of the IRNSS constellation of eight satellites (with one being a replacement). Three satellites are located in the geostationary orbit and the remaining four are located in geosynchronous orbits.
Applications
- Applications of IRNSS include:
- Terrestrial, Aerial and Marine Navigation
- Disaster Management
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management
- Integration with mobile phones
- Precise Timing
- Mapping and Geodetic data capture
- Terrestrial navigation aid for hikers and travellers
- Visual and voice navigation for drivers
Why in News?
- Vice President M Venkaiah Naidu suggested to ISRO to give a thrust to the indigenously-developed regional navigation satellite system, NaVIC for global use.
- He urged ISRO to actively pursue the expansion of the NaVIC system in terms of areas covered, services offered and its effective utilization to meet the national requirements.
Reference:
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
