Vehicle Scrappage Policy and its key features
Context:
- The government has recently introduced a vehicle scrappage policy to phase out old and defective vehicles.
The key features of the new policy:
- When an old vehicle is scrapped, the owner of such vehicle will receive the scrap value given by the scrapping centre, which is around 4-6 percent of the ex-showroom price of the new vehicle they buy.
- The scheme will provide incentives to the owners of the old vehicles to scrap their unfit vehicles through registered scrapping centres, which shall provide the owners with a scrapping certificate.
- The policy advises automobile manufacturers to provide a discount of 5 per cent on the purchase of a new vehicle against the scrapping certificate.
- The new policy also advises offering a road-tax rebate of up to 25 per cent for personal vehicles and up to 15 per cent for commercial vehicles.
- The new vehicle scrappage policy proposes Private Vehicles to be de-registered after 20 years if found unfit or in case of a failure to renew registration certificate. As a disincentive measure, increased re-registration fees will be applicable for private vehicles 15 years onwards from the date of initial registration.
- For commercial vehicles, the de-registration process starts after 15 years in case of failure to get the fitness certificate.
- In addition, the registration fees may also be waived for the purchase of a new vehicle against the scrapping certificate.
- Mandatory fitness testing of commercial vehicles is likely to start from April 1, 2023, while for personal vehicles it is expected to begin from June 1, 2024, in a phased manner.
Why should I scrap?
- To help vehicle owners find a reason to retire old vehicles, the government envisages that the scrappage certificate will entitle the owner with something extra, such as a tax rebate, sops, and a discount on the new car.
- The certificate is tradable, which means it can be used by anyone and not necessarily by the owner of the scrapped vehicle.
Does it help the economy?
- Globally, a scrappage policy has been followed by a boost in demand in the auto manufacturing sector, especially in Europe and the US.
- This has also been a tool to deal with economic slowdown in the manufacturing sector and consumption due to recession. Besides, there are spelt-out benefits vis-à-vis the environment since newer cars come with better emission standards and better fuel efficiency.
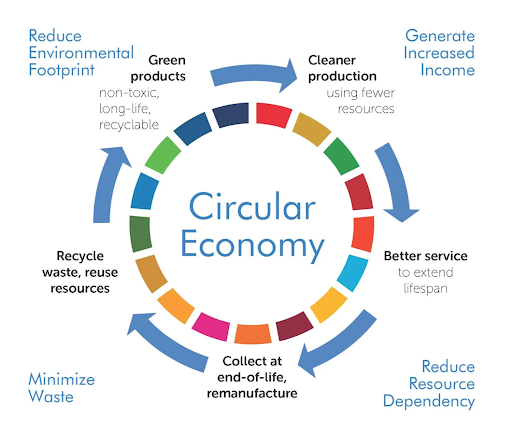
Concept of circular economy?
- A circular economy depends on reuse, sharing, repair, refurbishment, remanufacturing and recycling of resources to create a closed-loop system, minimising the use of resources, generation of waste, pollution and carbon emissions.
- When a car is scrapped, apart from metals including iron and steel, many other parts may emerge that can be refurbished and ploughed back into use.
- Recycled steel from scrap, even seats and plastic parts, have value in the scrap economy. It is similar to the economic activity of scrapping of old ships, like in Alang shipbreaking yard in Gujarat.
- In a circular economy, products, materials, equipment and infrastructure are kept in use for longer, thus improving productivity.
References:
- https://indianexpress.com/article/business/vehicle-scrappage-policy-launched-pm-narendra-modi-a-look-at-its-key-features-7452197/
- https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/vehicle-scrapping-policy-indian-economy-environment-7452803/
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
