Israel-Palestine conflict
What’s in the news?
- Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu warned that Israel’s response would be “very powerful” if Hamas violated the truce that ended conflict with the Gaza militants.
- Recently, Israel and Hamas (the militant Islamist group that rules the Gaza Strip) called a truce and agreed to a ceasefire, halting 11-days of hostilities that brought about widespread destruction in the Gaza Strip and left over 200 people dead.
- The latest violence followed a month of rising tensions in Jerusalem. But the fighting has gone on for decades.
Background
- Britain took control of the area known as Palestine after the ruler of that part of the Middle East, the Ottoman Empire, was defeated in World War 1.
- The land was inhabited by a Jewish minority and Arab majority.
- Tensions between the two peoples grew when the international community gave Britain the task of establishing a “national home” in Palestine for Jewish people.
- For Jews, it was their ancestral home, but Palestinian Arabs also claimed the land and opposed the move.
- Between the 1920s and 40s, the number of Jews arriving there grew, with many fleeing from persecution in Europe and seeking a homeland after the Holocaust of WWII. Violence between Jews and Arabs, and against British rule, also grew.
- In 1947, the UN voted for Palestine to be split into separate Jewish and Arab states, with Jerusalem becoming an international city.
- That plan was accepted by Jewish leaders but rejected by the Arab side and never implemented.
The creation of Israel and the ‘Catastrophe’
- In 1948, unable to solve the problem, British rulers left and Jewish leaders declared the creation of the state of Israel.
- Many Palestinians objected and a war followed. Troops from neighbouring Arab countries invaded. Hundreds of thousands of Palestinians fled or were forced out of their homes in what they call Al Nakba, or the “Catastrophe”.
- By the time the fighting ended in a ceasefire the following year, Israel controlled most of the territory. Jordan occupied land which became known as the West Bank, and Egypt occupied Gaza.
- Jerusalem was divided between Israeli forces in the West, and Jordanian forces in the East.
- Because there was never a peace agreement – each side blamed the other – there were more wars and fighting in the decades which followed.
The map today
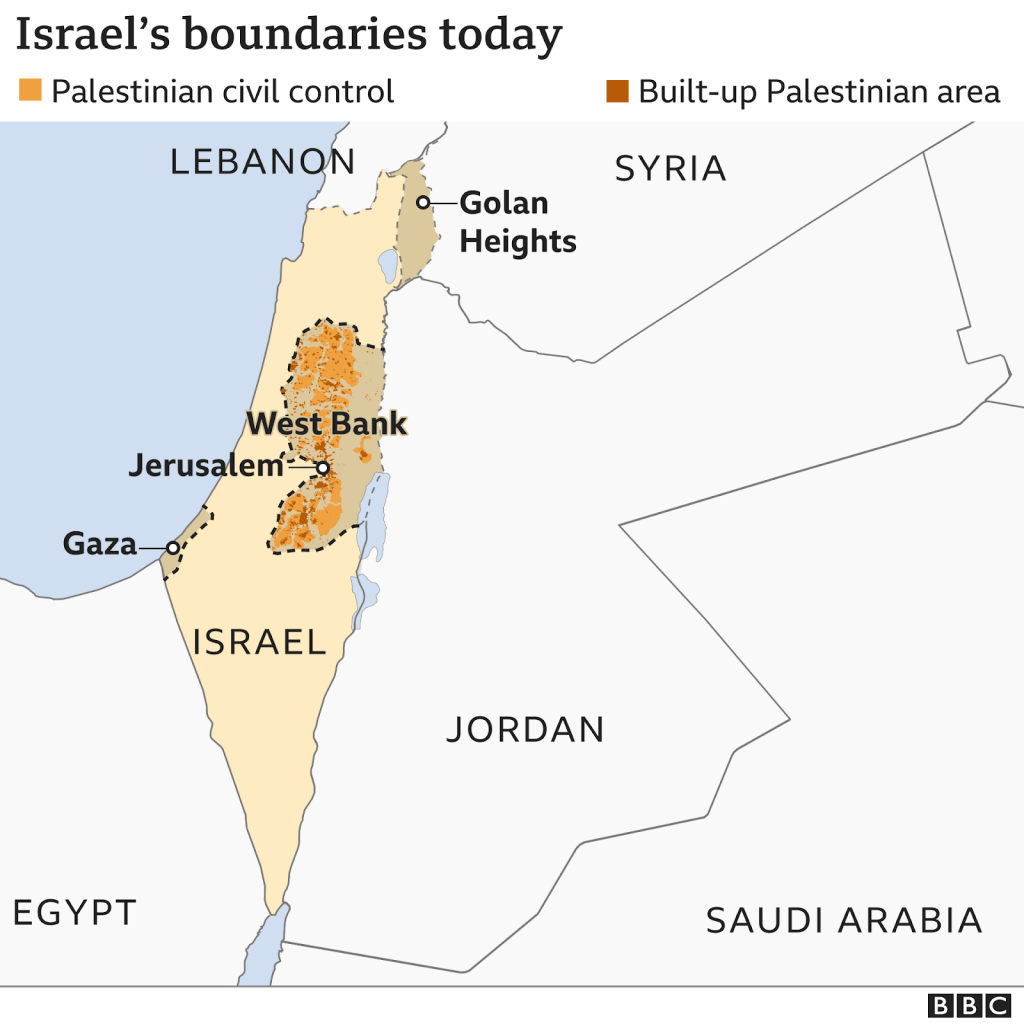
- In another war in 1967, Israel occupied East Jerusalem and the West Bank, as well as most of the Syrian Golan Heights, and Gaza and the Egyptian Sinai peninsula.
- Most Palestinian refugees and their descendants live in Gaza and the West Bank, as well as in neighbouring Jordan, Syria and Lebanon.
- Neither they nor their descendants have been allowed by Israel to return to their homes – Israel says this would overwhelm the country and threaten its existence as a Jewish state.
- Israel still occupies the West Bank, and although it pulled out of Gaza the UN still regards that piece of land as part of occupied territory.
- Israel claims the whole of Jerusalem as its capital, while the Palestinians claim East Jerusalem as the capital of a future Palestinian state. The US is one of only a handful of countries to recognise Israel’s claim to the whole of the city.
- In the past 50 years Israel has built settlements in these areas, where more than 600,000 Jews now live.
- Palestinians say these are illegal under international law and are obstacles to peace, but Israel denies this.
What’s happening now?
- Gaza is ruled by the Palestinian militant group Hamas, which has fought Israel many times. Israel and Egypt tightly control Gaza’s borders to stop weapons getting to Hamas.
- Palestinians in Gaza and the West Bank say they’re suffering because of Israeli actions and restrictions. Israel say it is only acting to protect itself from Palestinian violence.
- Things have escalated since the start of the holy Muslim month of Ramadan in mid-April 2021, with nightly clashes between police and Palestinians.
- The threatened eviction of some Palestinian families in East Jerusalem has also caused rising anger.
What are the main problems?
- There are a number of issues which Israel and the Palestinians cannot agree on.
- These include what should happen to Palestinian refugees, whether Jewish settlements in the occupied West Bank should stay or be removed, whether the two sides should share Jerusalem, and – perhaps most tricky of all – whether a Palestinian state should be created alongside Israel.
- Peace talks have been taking place on and off for more than 25 years, but so far have not solved the conflict.
What does the future hold?
- The UN and majority of the countries are pushing for the “two-state solution” to the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. Its basis is two separate states, Israel and Palestine, living peacefully side by side on the land between the western bank of the Jordan river and the Mediterranean Sea.
- This territory would be divided broadly along the pre-1967 armistice line or “green line”. Jerusalem, which both sides want as their capital, would be shared.
- Past negotiations have failed to make progress and there are currently no fresh talks in prospect.
- The most recent peace plan, prepared by the United States, when Donald Trump was President – called “the deal of the century” by Israeli PM Benjamin Netanyahu – has been dismissed by the Palestinians as one-sided and never got off the ground.
- Any future peace deal will need both sides to agree to resolve complex issues.
Reference:
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
