Cyclones
Why in News:
- The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) has forecast 2021’s first cyclonic storm in the Arabian Sea.
What are cyclones
- A cyclone is a system of winds rotating around a low pressure center. The swirling air rises and cools, creating clouds and precipitation.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, they bend to the right. This makes the cyclone rotate counterclockwise.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, currents bend to the left. This makes cyclones rotate clockwise.
- Cyclones are shaped clockwise/anti-clockwise by the Coriolis effect. The rotation of the earth about its axis affects the direction of the wind and this force is called the Coriolis force. The Coriolis effect is caused by our planet’s rotation.
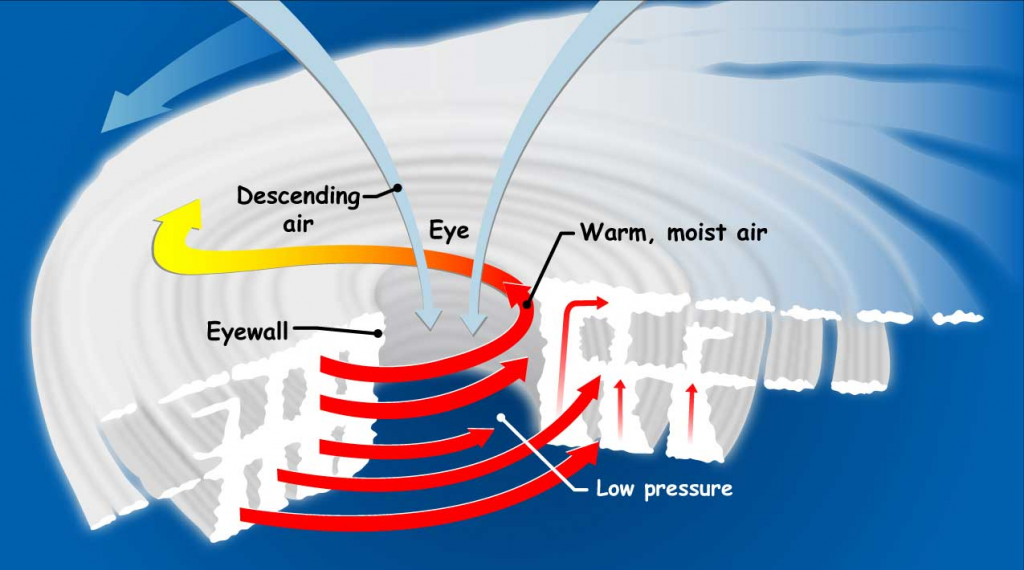
- The small red arrows show warm, moist air rising from the ocean’s surface, and forming clouds in bands around the eye. The blue arrows show how cool, dry air sinks in the eye and between the bands of clouds. The large red arrows show the rotation of the rising bands of clouds.
How are they formed
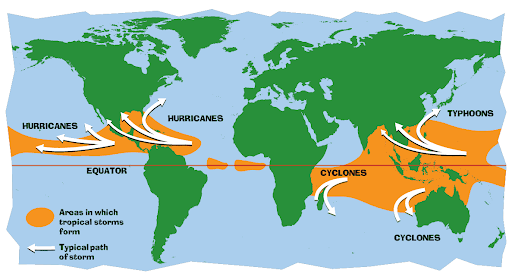
- Tropical cyclones are formed over warm ocean water near the equator.
- Warm moist air near the surface of the ocean rises upwards. This creates a low-pressure area near the surface.
- This results in the movement of cooler air from surrounding areas into the low-pressure area. Now even this cool air becomes warm and moist and rises up.
- The above cycle keeps continuing. The warm moist air which rises up, cools the water in the air, resulting in the formation of clouds. This whole system of clouds and winds spins and grows. This entire cycle continues resulting in a cyclone.
- When the winds reach a speed of 101 kmph, it is called a tropical storm, when the winds reach a speed of 119 kmph it is called a tropical cyclone or hurricane.
- There are various types of cyclones depending on the type of prevailing low-pressure system.
- Tropical cyclone
- Extratropical cyclone(Temperate cyclones are also known as Extra-tropical cyclones where the term “Extra-tropical” signifies that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside the tropics with a latitude range between 30° and 60°.)
- Tornadoes(A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud)
- Cyclones are addressed by different names in different locations.
- Hurricanes – In the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific.
- Typhoons – In Southeast Asia
- Cyclone – In the Indian Ocean and Western Pacific around Australia.
Related Information
Anticyclones
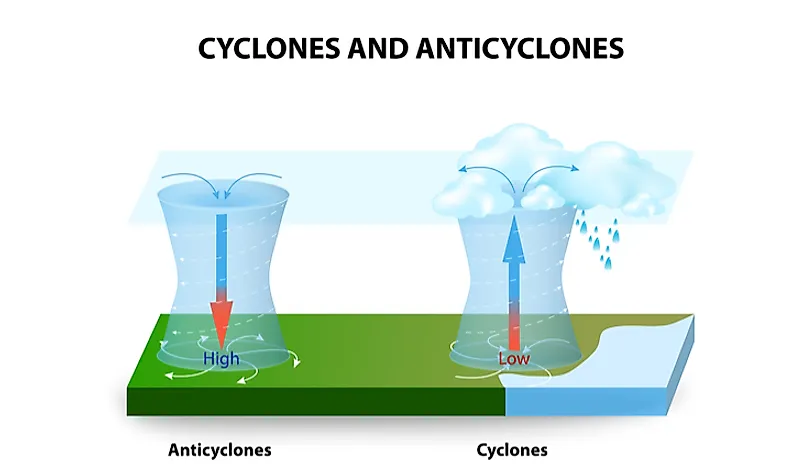
- An anticyclone is the opposite of a cyclone, which has an outward-spiralling air circulation around a high pressure centre.
- An anticyclone’s winds rotate clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere around a center of high pressure.
- In anticyclones, air comes in from above and sinks to the ground.
Reference:

[…] To know more about how cyclones are formed: https://officerspulse.com/cyclones/ […]
[…] To read about types of Cyclones & its formations – https://officerspulse.com/cyclones/ […]