What is a 5G trial, and why is it important for Indian telcos?
Importance of 5G Technology
- 5G or fifth generation is the latest upgrade in the long-term evolution (LTE) mobile broadband networks.
- 5G uses a new digital technology called Massive MIMO, which stands for multiple input multiple output, that uses multiple targeted beams to spotlight and follow users around a cell site, improving coverage, speed and capacity.
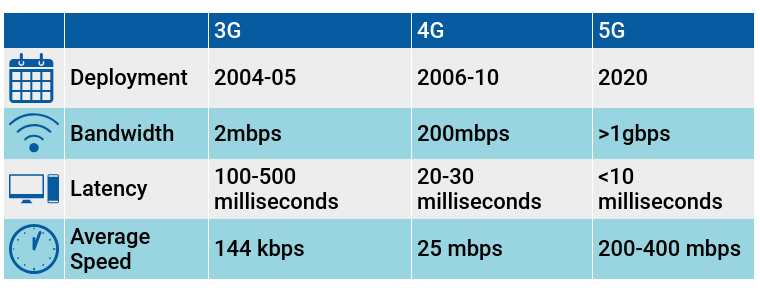
- The three major benefits offered by 5G are higher speeds, higher bandwidth and lower latency.
Speed
- Speed is one of the most highly anticipated elements of the 5G network which is expected to be nearly 100 times faster than 4G.
- Such high speeds are possible because most 5G networks are to be built on super-high-frequency airwaves, also known as high-band spectrum.
- The higher frequencies can transmit much more data, much faster than on 4G.
Capacity
- The 5G network is expected to have significantly more capacity than 4G.
- This is because 5G will have greater bandwidth, meaning it can handle many more connected devices than previous networks.
- It will bring in an “internet of things” era, filled with connected toothbrushes, kitchen appliances, street lamps and more.
Latency
- Latency is the time it takes for devices to communicate with each other or with the server that’s sending them information.
- Latency is already low with 4G, but 5G will make it virtually zero.
- It will be essential for technologies such as self-driving cars which require instant communication of huge data to ensure safety of its passengers.
How is latency different from speed?
- A small but significant difference exists between speed and latency.
- Speed is the amount of time it takes to download the contents of a webpage.
- Latency is the time between when a text is sent to another phone and when that receiver’s phone registers that it has received a new message.
Are there any drawbacks?
- The high-band network signals don’t travel very far and struggle to move through hard surfaces.
- In order to compensate for those challenges, wireless carriers building high-band 5G networks are installing tons of small cell sites (about the size of pizza boxes) to light poles, walls or towers, often in relatively small proximity to one another. For that reason, most carriers are deploying 5G city by city.
- Significant adoption of 5G is going to take years — industry trade group GSMA estimates that by 2025, around half of mobile connections will be 5G (the rest will be older tech, like 4G and 3G).
- There are also concerns among regulators and others about the security of 5G, especially since crucial technologies such as self-driving cars and healthcare systems will be built on top of the network.
Why in the News?
- The Department of Telecommunications has allowed private telcos Bharti Airtel, Reliance Jio Infocomm and Vi (formerly Vodafone Idea) and well as state-run telco Mahanagar Telephone Nigam Limited (MTNL) to start trials for 5G technology as well as its applications in various sectors.
Why are the trials for 5G technology important for telcos?
- 5G is the latest upgrade in the long-term evolution of mobile broadband networks. 5G mainly works in 3 bands, namely low, mid and high-frequency spectrum — all of which have their uses and limitations.
- In order to increase their average revenue per user, it is pertinent for telcos to start offering the new 5G technology as soon as possible.
What will 5G trials in India entail for now?
- For the six months period, the telcos will be provided with experimental spectrum in various bands, such as the mid-band of 3.2 GHz to 3.67 GHz, the millimeter wave band of 24.25 GHz to 28.5 GHz, and others.
- While the low band spectrum has shown great promise in terms of coverage and speed of internet and data exchange, the maximum speed is limited to 100 Mbps (Megabits per second).
- The mid-band spectrum, on the other hand, offers higher speeds compared to the low band, but has limitations in terms of coverage area and penetration of signals.
- The high-band spectrum offers the highest speed of all the three bands, but has extremely limited coverage and signal penetration strength. Internet speeds in the high-band spectrum of 5G have been tested to be as high as 20 Gbps (gigabits per second), while, in most cases, the maximum internet data speed in 4G has been recorded at 1 Gbps.
Reference:
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
