A shift in Earth’s axis
Why in News?
- A recent study has noted that due to the significant melting of glaciers because of global temperature rise, our planet’s axis of rotation has been moving more than usual since the 1990s.
Cause for this shift
- According to NASA, data from the 20th century shows that the spin axis drifted about 10 centimetres per year. Meaning over a century, polar motion exceeds 10 metres.
- The possible causes are (terrestrial water storage) change in non‐glacial regions due to climate change and unsustainable consumption of groundwater for irrigation and other anthropogenic activities.
- Generally, polar motion is caused by changes in the hydrosphere, atmosphere, oceans, or solid Earth. But now, climate change is adding to the degree with which the poles wander.
- While ice melting is the major factor behind increased polar motion, groundwater depletion also adds to the phenomenon. As millions of tonnes of water from below the land is pumped out every year for drinking, industries or agriculture, most of it eventually joins the sea, thus redistributing the planet’s mass.
What the new study says?
- Since the 1990s, climate change has caused billions of tonnes of glacial ice to melt into oceans. This has caused the Earth’s poles to move in new directions.
- As per the study, the north pole has shifted in a new eastward direction since the 1990s, because of changes in the hydrosphere (meaning the way in which water is stored on Earth). From 1995 to 2020, the average speed of drift was 17 times faster than from 1981 to 1995. Also, in the last four decades, the poles moved by about 4 metres in distance.
- The calculations were based on satellite data from NASA’s Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) mission as well as estimates of glacier loss and groundwater pumping going back to the 1980s.
- The faster ice melting under global warming was the most likely cause of the directional change of the polar drift in the 1990s.
What is the effect of this shift?
- While this change is not expected to affect daily life, it can change the length of the day by a few milliseconds.
Related information
What is the Earth’s Axis
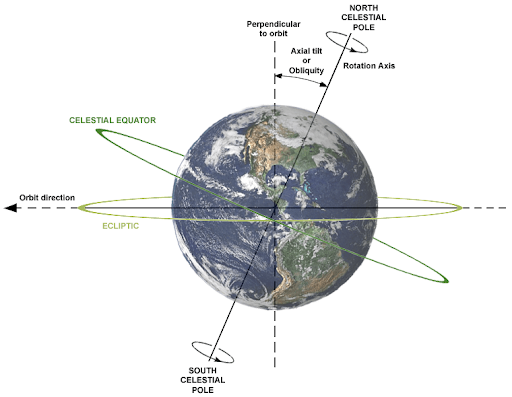
- Earth’s Axis is the line along which it spins around itself as it revolves around the Sun.
- Earth’s axial tilt (also known as the obliquity of the ecliptic) is about 23.5 degrees.
- Due to this axial tilt, the sun shines on different latitudes at different angles throughout the year. And this is why we have different seasons. The points on which the axis intersects the planet’s surface are the geographical north and south poles.
Are these poles fixed?
- The axis moves due to changes in how the Earth’s mass is distributed around the planet and hence the location of poles is not fixed. Thus, the poles move when the axis moves, and this movement is called “polar motion”.
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
