What is bird flu and how severe is the latest outbreak in India?
Why in the news?
- Bird flu is affecting domestic and wild birds all over India. Wild geese in Himachal Pradesh, crows in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh, ducks in Kerala and poultry birds in Haryana are victims of bird flu.
What is bird flu?
- Bird flu, also called avian influenza, is a viral infection that can infect not only birds, but also humans and other animals. Most forms of the virus are restricted to birds.
- H5N1 is the most common form of bird flu. There are many strains of the virus – some of them are mild and may merely cause a low egg production or other mild symptoms among chickens, while others are severe and lethal.
- It’s deadly to birds and can easily affect humans and other animals that come in contact with a carrier.
What is the source of the flu?
- Wild water birds (like ducks and geese) can be infected with bird flu viruses, but usually do not get sick. Infected birds have viruses in their saliva, mucous and droppings (feces).
- From water birds, many of whom migrate and travel long distances, the viruses are thus further spread to poultry and terrestrial birds. Sometimes, the virus jumps over to mammals such as pigs, horses, cats and dogs.
- Movement of infected poultry and migratory birds, and an illegal bird trade are believed to be the causes of the spread of bird flu. Since birds excrete even while flying, they provide a nice aerosol of influenza virus, shedding it all over the world.
- Bird flu viruses spread easily between birds. Some of these viruses can cause serious illness and death in domestic poultry (like chickens, ducks and turkeys).
Measures taken to stop bird flu
- Generally poultry birds are vaccinated against the disease. But if found in large numbers, culling of birds is done to stop the spread.
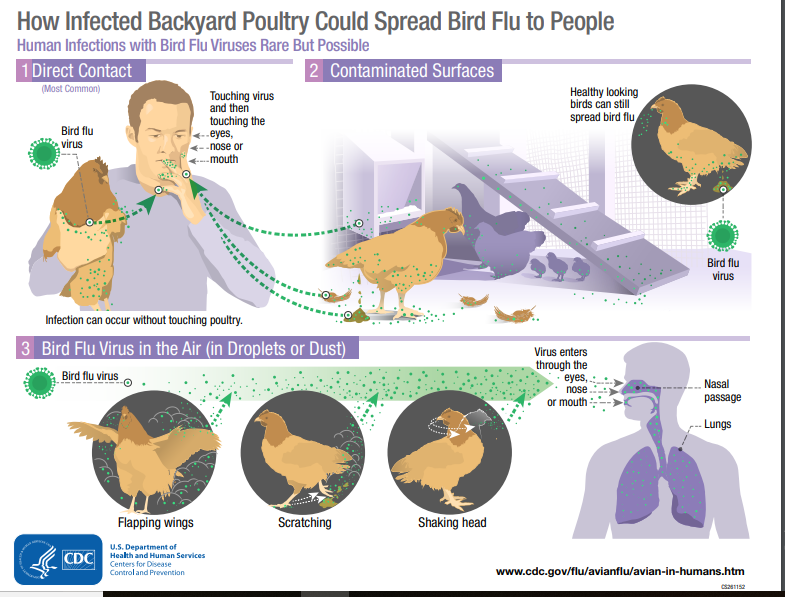
Bird Flu and Humans
- According to the World Health OrganizationTrusted Source, H5N1 was first discovered in humans in 1997 and has killed nearly 60 percent of those infected.
- Unlike in birds, where it generally infects the gut, the avian influenza attacks the respiratory tract of humans and may cause severe respiratory illnesses such as pneumonia or Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). Its early symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, and sometimes abdominal pain and diarrhoea.
- According to WHO, the disease does not spread among humans. There is also no evidence that the disease spread from poultry food. Virus is sensitive to heat and dies in cooking temperatures.
Way Forward
- Flu viruses are more prone to mutation because they have a segmented genome (there are several fragments of genetic material that make a complete virus genome). All known strains of flu – including the seasonal flu and the pandemic flu – have jumped from birds to humans.
- If the virus mutates and becomes easily transmissible from person to person, say by altering its shape to grab human cells much more effectively, it can potentially cause a pandemic.
- Among poultry birds, vaccination strategies advised by the World Organisation for Animal Health can be used to prevent the flu, and the Organisation recommends eradicating the highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) at its source to decrease the disease in avian species and further human infections.
References:
- https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/what-is-bird-flu-and-how-severe-is-the-latest-outbreak-in-india-7133945/
- https://www.healthline.com/health/avian-influenza#prevention
- https://www.cdc.gov/flu/pdf/avianflu/avian-flu-transmission.pdf
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
