Newly identified tectonically active zone in Himalayas
What is a tectonic plate?
- A tectonic plate (also called lithospheric plate) is a massive, irregularly-shaped slab of solid rock, generally composed of both continental and oceanic lithosphere.
- Plates move horizontally over the asthenosphere (the ductile part of the earth just below the lithosphere, including the upper mantle) as rigid units.
- The lithosphere includes the crust and top mantle with its thickness range varying between 5-100 km in oceanic parts and about 200 km in the continental areas.
- A plate may be referred to as the continental plate or oceanic plate depending on which of the two occupy a larger portion of the plate.
- The movement of these crustal plates causes the formation of various landforms and is the principal cause of all earth movements.
The major plates are as follows :
Some important minor plates are listed below:
|
Why in News?
-
- The suture zone of the Himalayas or the Indus Suture Zone (ISZ) in the Ladakh region where Indian and Asian Plates are joined has been found to be tectonically active, as against current understanding that it is a locked zone.
- A suture zone is a linear belt of intense deformation, where distinct terranes, or tectonic units with different plate tectonic, metamorphic, and paleogeographic histories join together.
- This could have major implications in terms of earthquake study, prediction, understanding the seismic structure of the mountain chains well as its evolution.
Relation between Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes:
- Tectonic plates are constantly shifting as they drift around on the viscous, or slowly flowing, mantle layer below. This non-stop movement causes stress on Earth’s crust. When the stresses get too large, it leads to cracks called faults.
- When tectonic plates move, it also causes movements at the faults. Thus, the slipping of land along the faultline along convergent, divergent and transform boundaries cause earthquakes.
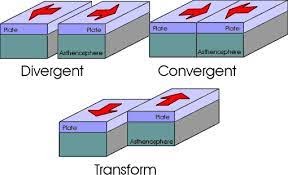
| Divergent Boundaries Where new crust is generated as the plates pull away from each other. The sites where the plates move away from each other are called spreading sites.
Convergent Boundaries Where the crust is destroyed as one plate dived under another. The location where sinking of a plate occurs is called a subduction zone. There are three ways in which convergence can occur. These are: (i) between an oceanic and continental plate; (ii) between two oceanic plates; and (iii) between two continental plates Transform Boundaries Where the crust is neither produced nor destroyed as the plates slide horizontally past each other. |
References:
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
