Abraham Accord and India
Context
- The formal normalisation of Israel’s ties with the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and the Kingdom of Bahrain has created a significant inflection point in regional history and geopolitics. This article deals with the impact of such ties of Israel on India.
About Abraham Accord
- Israel, Bahrain and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) recently announced that they will normalise diplomatic relations and the agreement is called the ‘Abraham Accord’ which was mediated by US President Donald Trump.
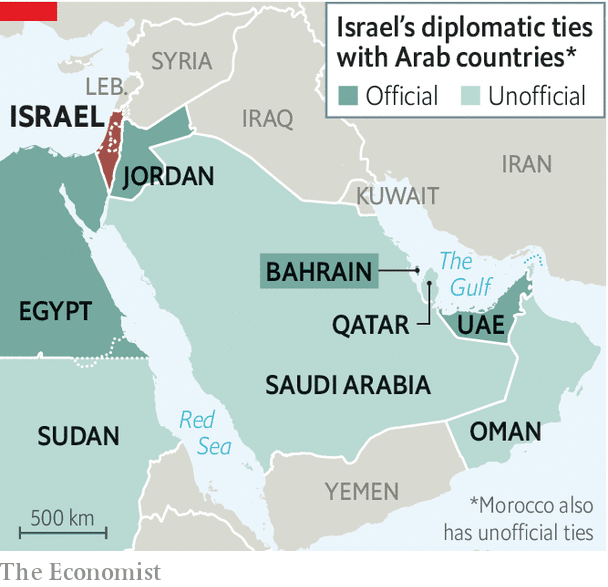
Previous agreements
- This move is significant because with the exception of Jordan and Egypt, Israel does not have diplomatic relations with Gulf Arab states owing to its long-standing conflict with Palestinians.
- Israel had signed peace agreements with Egypt in 1979 and with Jordan in 1994.
Nuances that make Abraham accord differ from the previous agreements
- The UAE and Bahrain do not have any territorial dispute with Israel, nor have they ever been at war with it.
- Although formally committed to an Arab consensus over a two-state resolution of the Palestine cause, these two countries have steadily moved towards having substantive links with Israel in recent years.
- Hence, the ‘Abraham Accords’ entered with the UAE and Bahrain are ‘peace-for-peace’ deals without any physical quid pro quo by Israel.
- Quid pro quo means a situation in which someone does something in exchange for something else.
Commonality between them
- Iran factor: Israel, the UAE and Bahrain share the common threat perception of Iran against the backdrop of the ongoing diminution of Pax Americana in the region.
- Economic revival: They are relatively more modern societies which share the overarching and immediate priority of post-pandemic economic resuscitation.
What does the UAE get out of it?
- The agreement enables the UAE to develop commercial, diplomatic and security ties with Israel while arguing it helped the Palestinians by getting Israel to halt annexation.
- The agreement could also give the UAE access to previously off-limits U.S. weaponry, such as advanced drones, just as Egypt was able to secure better American arms after its peace deal with Israel.
- It also gives the UAE an opportunity to collaborate on technology and health care with Israel, a leader in both, at a time when combating Covid-19 is every country’s chief concern.
What does Israel get?
- For Israel, establishing normal diplomatic ties with Arab countries has long been a strategic goal.
- It signals greater acceptance in the Middle East and the potential for more commercial ties for a country that has until now conducted very little of its business in its own region.
What does Bahrain get out of it?
- As per the agreements Bahrain will establish embassies, exchange ambassadors, cooperate and work together with Israel across a range of sectors, including tourism, trade, healthcare and security.
India and the gulf
- It is natural to ask how the new regional dynamic would affect India as India has
- Over eight million Indian diaspora in the Gulf remit nearly $50 billion
- Annual merchandise trade of over $150 billion with the gulf
- Nearly two-thirds of India’s hydrocarbon imports are being sourced
- Major investments in gulf
Implications for India
- Israel’s agreement with Egypt and Jordan did not have any major impact on India as our ties with them were relatively insignificant. However, now India has stronger, multifaceted and growing socio economic engagements with Israel and the Gulf countries.
Geopolitical significance
- Geopolitically, India has welcomed the establishment of diplomatic relations between the UAE and Israel, calling both its strategic partners.
Ease India’s diplomacy
- The Israel-Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) breakthrough widens the moderate constituency for peaceful resolution of the Palestine dispute, easing India’s diplomatic balancing act.
New arena of proxy war
- The Southern Gulf can become the new arena of the proxy war between Iran and Israel which necessitates India to be on its guard to monitor such events.
Economic challenges
- India has acquired a large and rewarding regional footprint, particularly as the preferred source of manpower, food products, pharmaceuticals, gem and jewellery, light engineering items, etc.
- But Israel has niche strengths in defence, security and surveillance equipment, arid farming, solar power, horticultural products, high-tech, gem and jewellery, pharmaceuticals and has the potential to supply skilled and semi-skilled manpower to the GCC states.
- Thus India has to manage the economic fallout of Israel- GCC synergy.
Conclusion
- In the evolving scenario, there may be scope for a profitable trilateral synergy, however Israel entering into the Gulf has the potential to disrupt the existing politico-economic architecture India has carefully built with the GCC states.
References:
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
